Biostat Cluster Quickstart Guide
This guide will get you up and running on the Biostat Cluster by providing information on various sign-in methods, transferring data, and submitting jobs.
On this page
Requesting an account
All members of the Biostatistics department are eligible to use the Biostatistics cluster for free. To request access to the cluster, please fill out this Google form.
Notice: As of Fall 2022, the Biostat cluster is no longer offering paid accounts.
Accessing the Cluster
The Biostatistics cluster may be accessed from the command line or from a graphical web portal. New cluster users who are not familiar with using Linux from the command line or the SSH protocol are encouraged to start with the graphical web portal as it has a smaller learning curve. The cluster may only be accessed from on campus using MWireless or from the University VPN.
Graphical Web Portal
The cluster's graphical web portal is accessible from any web browser. Simply navigate
to biostat-login.sph.umich.edu and log in with your University credentials. After you log in, you will see the portal
home page. From the portal home page, you can select an application from the top menu
bar. More on each application can be found below in this guide.
Command Line
SSH from A Windows computer
The following is an example of connecting to the cluster from a computer running the Windows operating system. Most modern version of Windows now come with OpenSSH, so you may use the PowerShell application to connect via SSH the same way you would with Linux or macOS (described below). Alternatively, you can use a third-party SSH client like PuTTY which can be downloaded from the ssh.com website.
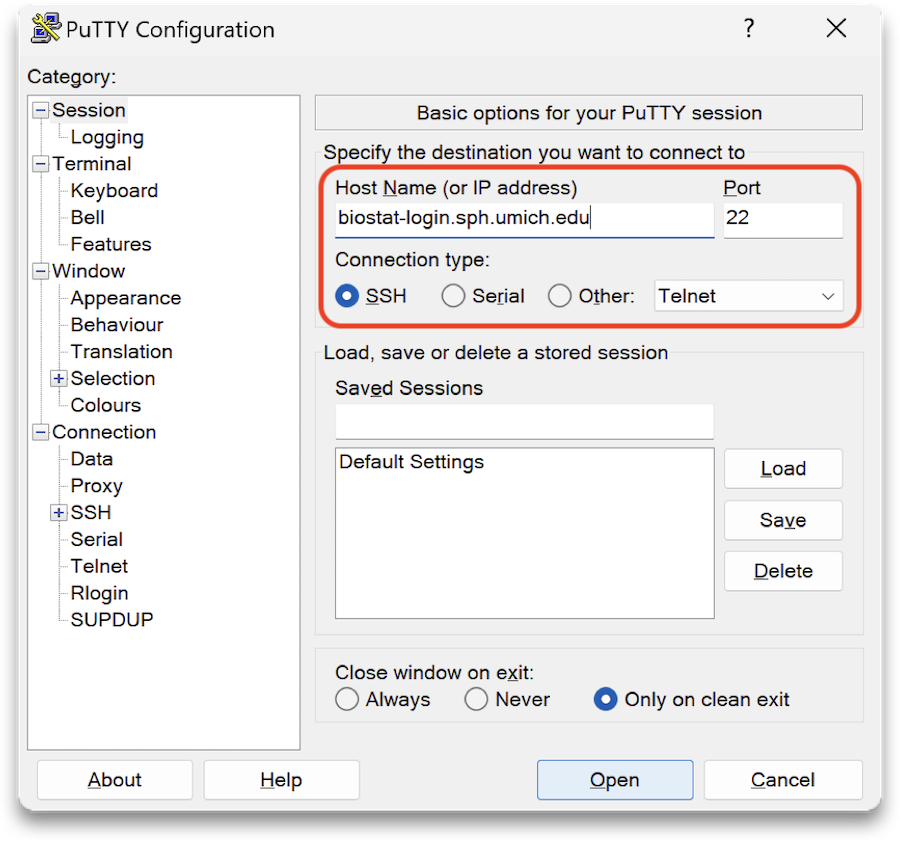
Once PuTTY is installed, launch the application and enter biostat-login.sph.umich.edu into the Host Name field, ensure SSH is selected, and then click Open.
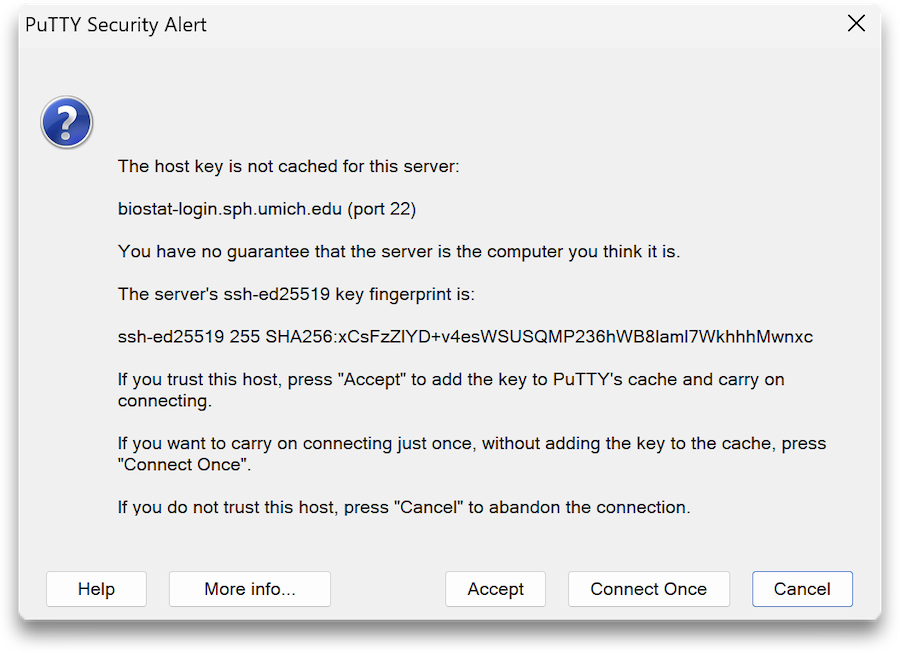
The first time you connect to the cluster you may see a warning — this is normal. Compare the fingerprint presented in the warning with the following:
Biostat Cluster SSH Key Fingerprint:
ED25519 SHA256:xCsFzZlYD+v4esWSUSQMP236hWB8lamI7WkhhhMwnxcIf they match, press Accept.
If they do not match, please contact [email protected].
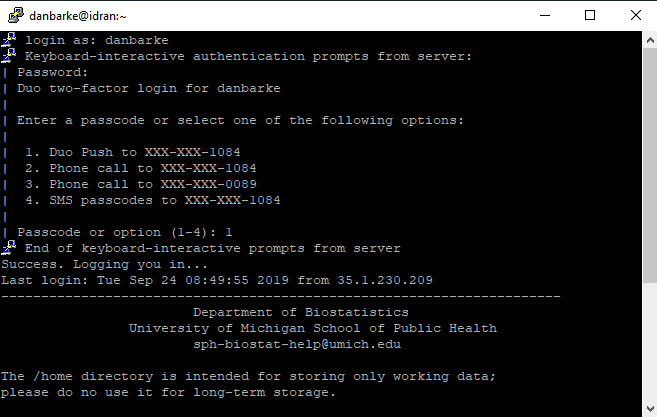
A terminal will open where you can login using your uniqname, kerberos password, and Duo two-factor. Note that as you type your password, nothing will appear on the password line. This is normal; just finish typing your password and hit "enter/return" on your keyboard.
SSH from a Mac or Linux Computer
The following is an example of connecting to the cluster from a computer running the macOS or Linux operating systems. Both macOS and Linux have an application called terminal. Once terminal is opened, the username that you want to connect as and the server that you wish to connect to must be specified.
Open a terminal window type ssh [email protected] and then hit enter/return on your keyboard. Replace uniqname with your University uniqname. You will be prompted for your University kerberos password. Note that as you type your password, nothing will appear on the password line. This is normal; just finish typing your password and hit "enter/return" on your keyboard. You will then be prompted to complete Duo two-factor authentication.
Copy scripts and data to the cluster
Your scripts and data files must be uploaded to the cluster in order to do any computing with them. The easiest way to upload files to the cluster is through the "files" application of the graphical web portal. Simply navigate to biostat-login.sph.umich.edu and login with your University Credentials. After you log in, you will see the portal home page. On the top menu bar select "Files" and then "Home Directory". This will open a new tab in which you can use the File Explorer application. This application allows you to upload files to the cluster, download files from the cluster, view and edit files and directories.
Creating a batch script
A batch script is a specially formatted text file that specifies to the cluster the resources (CPUs, Memory, time) that the job will need. At the bottom of the batch script is a line that calls the script that should be executed. Batch scripts may be created locally on your computer and uploaded to the cluster, or they may be created directly on the cluster using the built-in file editor.
Below is a quick sample batch script for running a single job with a default resource allocation of 1 CPU and 1000MB of memory running for 1 hour. It will execute an R script named script.R.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name=hello_world
#SBATCH --time=1:00:00
#SBATCH [email protected]
#SBATCH --mail-type=END,FAIL,BEGIN,NONE
#SBATCH --mem=1000m
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1
R CMD BATCH --no-save --no-restore script.RSubmitting your job
Assuming you saved the above batch script to job.txt in your home directory you can submit the job with sbatch:
$ sbatch job.txt
If successfully submitted, you will see the job id for the job you just submitted and will receive an email when the job starts, when it ends, and if it should fail.
Checking the status of your job
You can check the status of your job in the queue with the squeue command:
$ squeue -u $USER
OR
$ sq